Migraine vs. Headaches. What is the Difference?

I recently attended a virtual talk by Gleneagles Hospital entitled “Headache and Migraine”. This talk was delivered by the hospital’s neurologist, Dr. Ooi Phaik Yee.
She first started off by defining what headaches are and how migraine is also classified as a headache. She shared more on the different types of migraines, symptoms and treatments out there to manage this condition.
It is no surprise that the main cause of headaches and migraines are stress. Around 80% of the population reported stress as the trigger for their condition.
What’s the Difference between Headaches and Migraines?
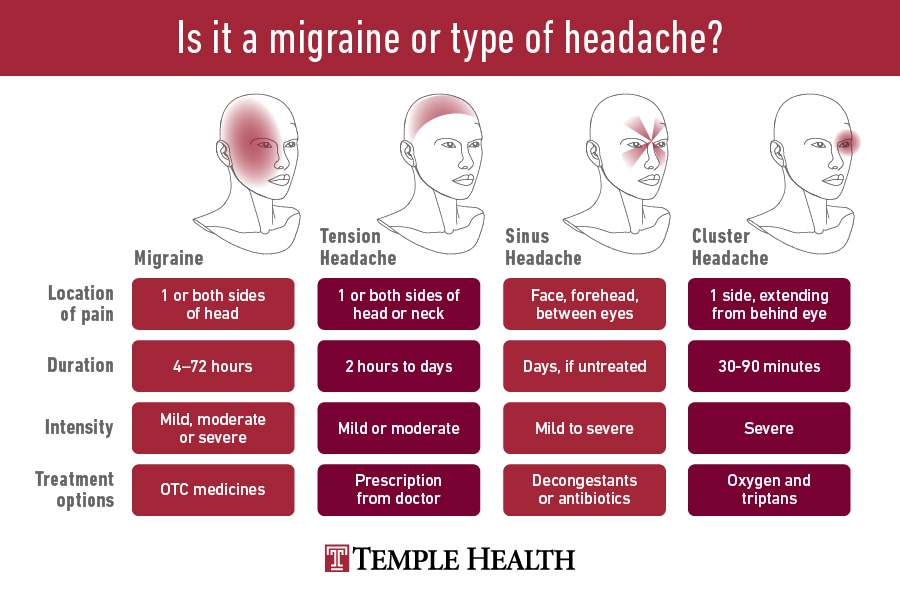
The term headache is a broad term used to classify pain or discomfort in the head and face area. Migraines are a type of headache where a throbbing pain is on one side of the face. Migraines can range from mild to severe and can last for hours to days.
Classification of Headaches
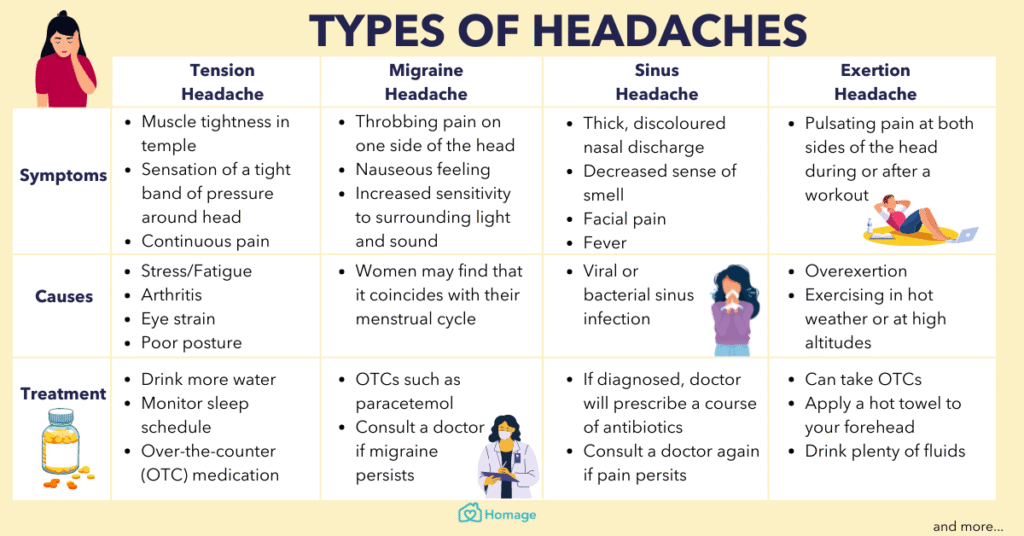
Headaches can be categorised into primary or secondary headaches.
Primary headaches are those with no identified cause such as migraine or tension-type headache. These are by far the most common type of headaches making up 98% of all headaches.
Secondary headaches are those which have an underlying health condition. The underlying health condition consists off head and neck trauma, substance abuse and cranial or cervical intravascular disorder.
Migraine Triggers

Most of the time, migraines do have a trigger hence it’s important to step back and relax when faced with the trigger. The common triggers are:
• Stress
• Hormonal changes
• Certain medications
• Changes in sleep pattern (usually sleep deprivation)
• Changes in weather from hot to cold or cold to hot
• Overexertion of body during physical activity
• Addictive substances like caffeine or tobacco.
• Missing a meal.
• Exposure to bright lights, loud noises or strong odors.
If you are not aware of your triggers, keep a migraine journal to note down the situations that may have triggered the condition.
What food triggers migraine?
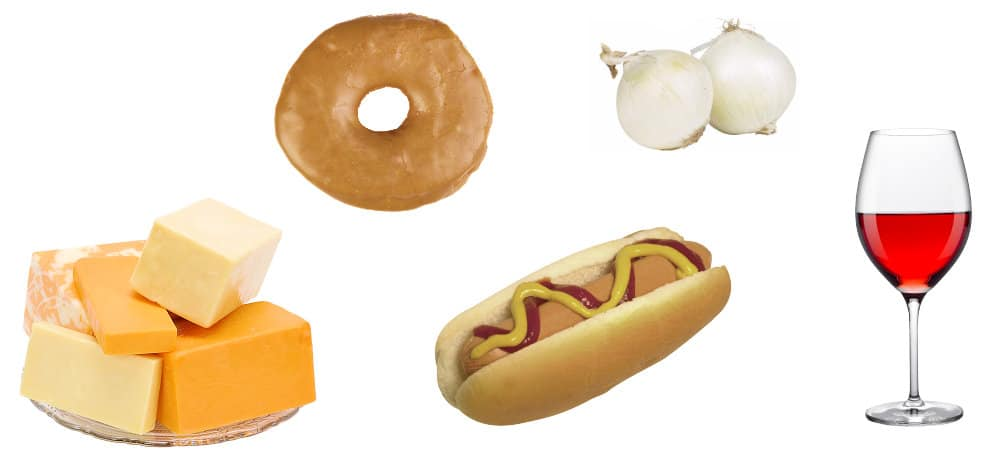

Besides situations, specific chemicals and preservatives in foods may also trigger migraine.
Some of the most common food triggers include:
• Aged cheese
• Alcoholic beverages
• Chocolate
• Food additives like nitrates and MSG
• Processed or cured foods (hot dogs, pepperoni)
• Fermented or pickled foods
Not forgetting, migraines are also genetic in nature with 80% of first degree relative having the health condition.
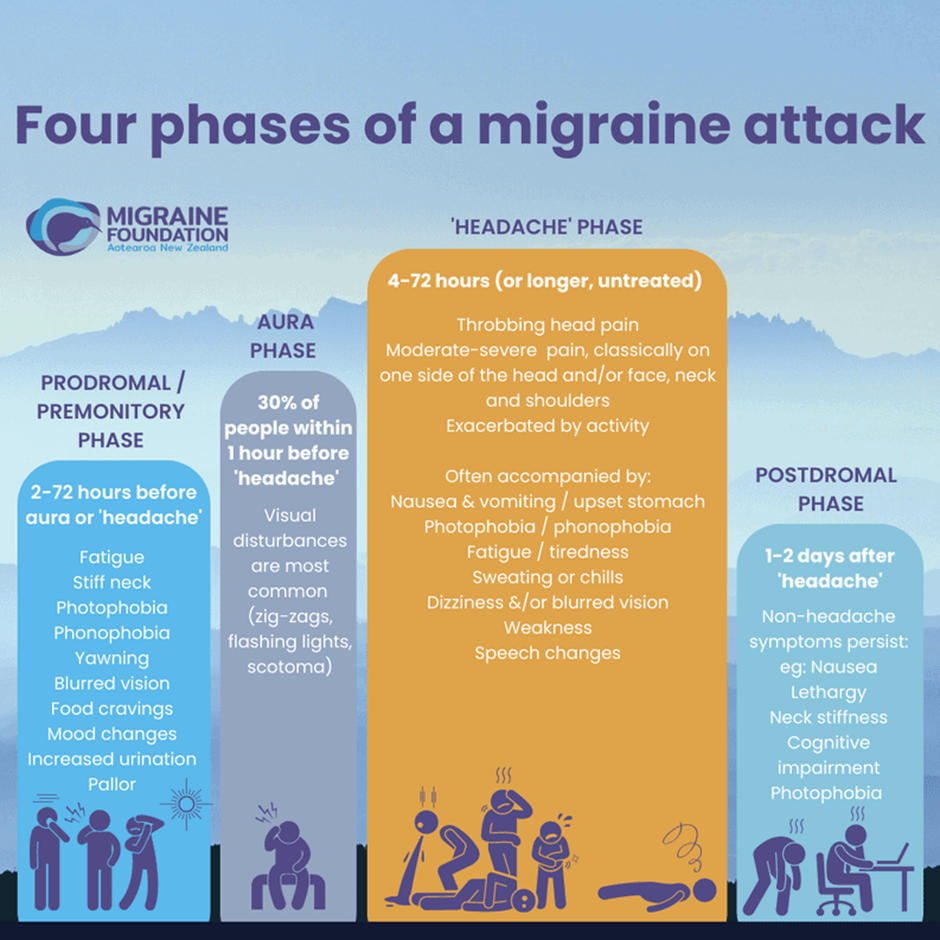
The Four Stages of Migraine
Migraines are different for each person but in general, there are four stages of a migraine attack: the prodromal stage, aura, headache pain, and postdrome stage. Not everyone goes through the 4 stages.
Below are the 4 stages of a migraine attack and the symptoms:
Treatments
People who have migraines occasionally may benefit from taking migraine reduction medications. Examples of these medications include anti-nausea medications, such as:
• promethazine (Phenergan)
• chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
• prochlorperazine (Compazine)
• mild to moderate pain relievers, such as acetaminophen
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as:
• aspirin
• naproxen sodium
• ibuprofen
• triptans, such as:
• almotriptan (Axert)
• rizatriptan (Maxalt)
• sumatriptan (Alsuma, Imitrex, and Zecuity)
If a person takes migraine medications more than 10 days a month, this could cause medication overuse headache. This practice will worsen their headache severity instead of helping them feel better.
Prevention Tips
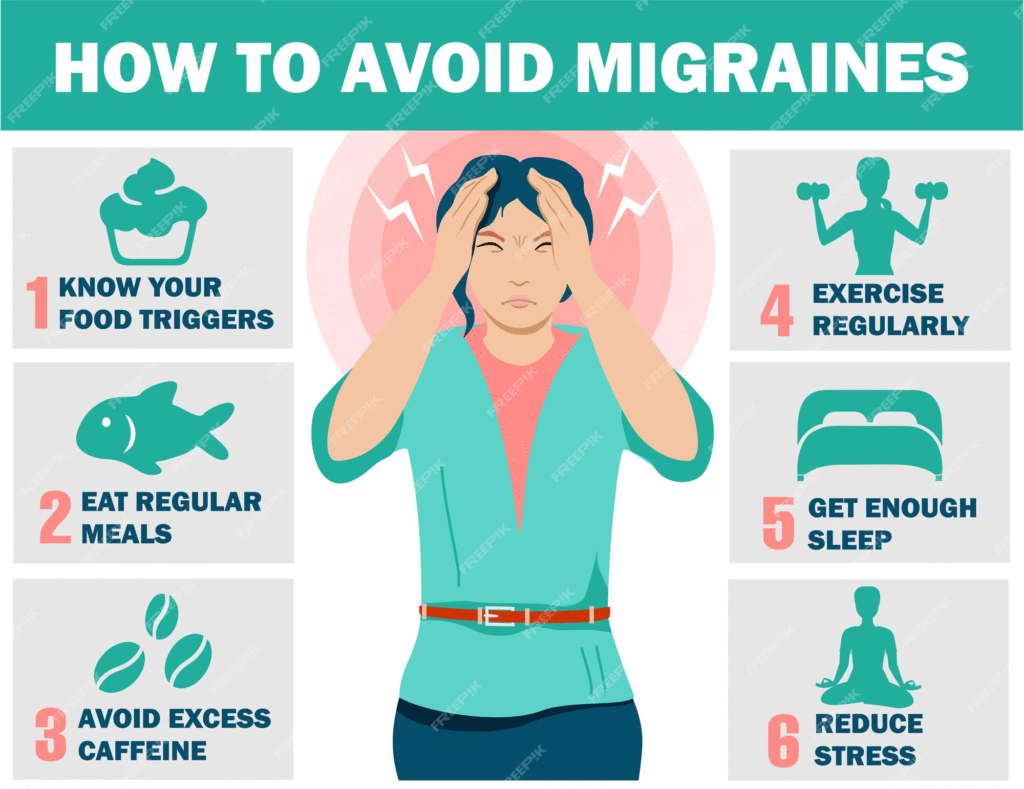
Prevention is often the best treatment for migraine episodes. Examples of preventive methods include:
a) making dietary changes such as eliminating foods and substances known to cause headaches, like alcohol and caffeine.
b) Taking daily prescription medications and not skipping any doses. Medications may include:
• antidepressants
• blood pressure-lowering medications
• anti-epileptic medications
• CGRP receptor antagonists
c) Taking steps to reduce stress, such as meditating and adopting relaxation techniques.
References:
1. Geeky Medics. Headache
2. Temple Health. Is It a Migraine or Headache?







