The Menopause Tales – All A Lady Needs to Know
Recently, I attended a panel discussing menopause woes. A gynae, the MD of the company and a moderator was seated to discuss this issue. It is not every day that a company takes interest in its staffs’ menopausal issues. However, this was made possible by the Managing Director (MD) who is currently undergoing menopause. The MD shared her experience dealing with hot flushes, poor sleep and other symptoms. The gynae also shared her experience dealing with menopausal ladies who are at the peak of their careers. She said many ladies could not cope with their body and emotional changes due to menopause and decide to resign from their jobs. This is a loss of talent.
What is Menopause?

Menopause is a point in time when one has gone 12 consecutive months without periods. It is a natural process that occurs to middle aged ladies and happens between the age of 48-55 years old with the average being 50 years old. Menopause occurs when the ovaries stop producing reproductive hormones. When menopause happens due to surgery or medical treatment, it’s called induced menopause.
Stages of Menopause
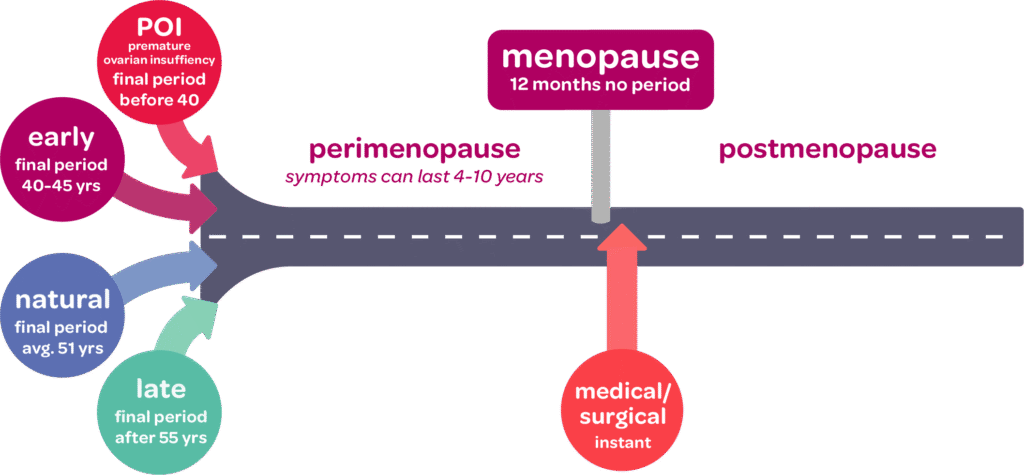
Usually, menopause is a gradual transition and could happen over a period of 10 years. This transition may span over 3 stages:
- Perimenopause: Perimenopause begins 8 to 10 years prior to menopause, and this usually starts in the early 40s. This happens when the ovary produces less oestrogen over time. At this point, many ladies start having symptoms of irregular periods, hot flashes and mood swings.
- Menopause: Menopause is the point where one no longer menstruates for more than 12 months. At this stage, the ovaries don’t release eggs anymore and oestrogen production is minimal. It is difficult to define menopause as one can move between the perimenopause to menopause stage ever so often. This means one gets their period for a few months and then proceeds not to get it for a year and then gets it again later. Symptoms may also vary between being present and absent.
- Postmenopause: This is a defined time where one stays in post-menopause for a lifetime. By this time, most symptoms of menopause have ceased and only the mild symptoms are present and this can continue for a few years. People in the postmenopausal phase are at an increased risk for osteoporosis and heart disease due to low oestrogen levels.
There is also a phase of premature menopause. This menopauseoccurs at the age of 40 and below. When there’s no medical diagnosis for premature menopause, its attributed to primary ovarian insufficiency. This means the ovary doesn’t make the typical amount of oestrogen hormone or release eggs regularly.
Common Menopause Signs & Symptoms
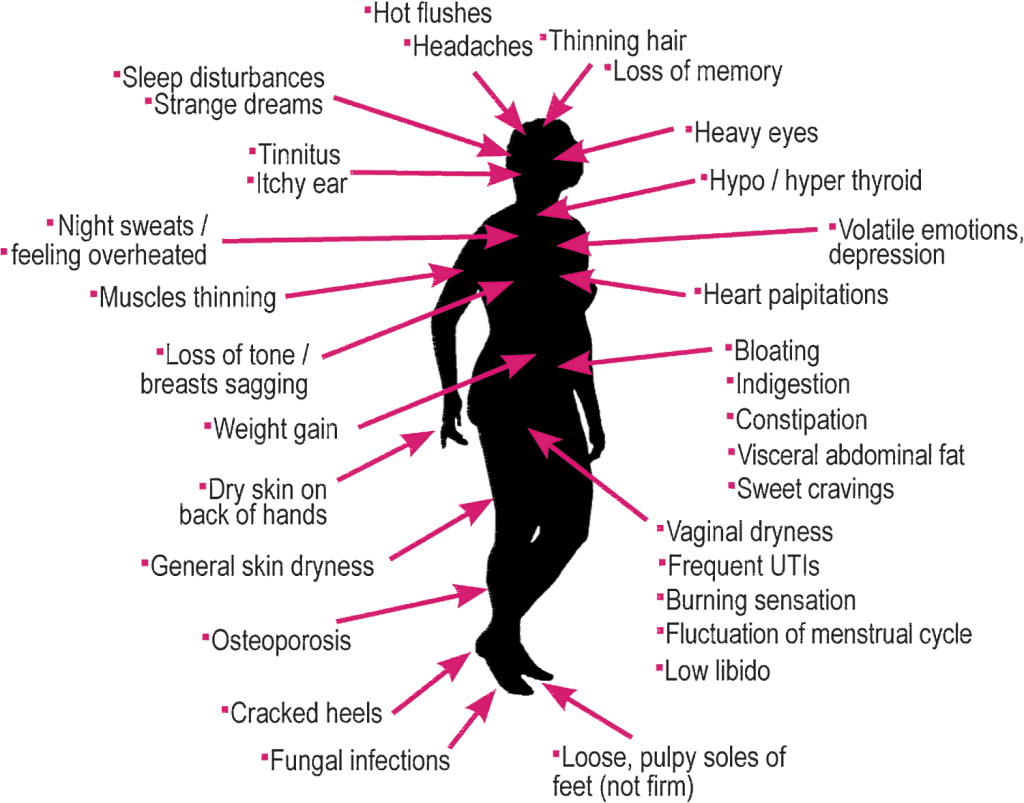
Depending on many factors, some women have heavy symptom loads during menopause while others have mild symptoms. Also, not every woman will have the same symptoms across the spectrum.
Usually, the start of menopause is marked by symptoms below:
- Irregular periods or periods that are heavier or lighter than usual
- Hot flashes (a sudden feeling of warmth that spreads over your body)
- Night sweats and/or cold flashes
- Vaginal dryness
- Urinary urgency (a pressing need to pee more frequently)
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Emotional changes (irritability, mood swings or depression)
- Dry skin, dry eyes or dry mouth
- Worsening premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Breast tenderness
Some people might also experience:
- Racing heart
- Headaches
- Joint and muscle aches and pains
- Changes in libido (sex drive)
- Difficulty concentrating or memory lapses (often temporary)
- Weight gain
- Hair loss or thinning
Treatment of Menopause
Treatment for menopause can be divided into hormonal and non-hormonal treatment.
Hormonal

During menopause, the body undergoes major hormonal changes where ovaries release minimal oestrogen and progesterone. This reduction of hormones causes symptoms like hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
Hormone therapy boosts the hormone levels in the body and help manage these symptoms thus reduce osteoporosis and risk of heart attack attributed to menopause.
There are two main types of hormone therapy:
- Estrogen therapy (ET): In this treatment, one takes a low dose oestrogen alone. This oestrogen may be administered many forms, such as a patch, pill, cream, vaginal ring, gel or spray. Oestrogen therapy can’t be used alone (without a progestogen) if one still has their uterus intact and has not undergone hysterectomy.
- Estrogen progestogen therapy (EPT): This is a combination therapy because it uses doses of estrogen and a hormone similar to progesterone to manage hormone levels. This therapy can only be used by those who still have their uterus intact.
With the multiple benefits of hormone therapy, there are also risks to it.
Non- Hormonal
Non-hormonal treatments involve lifestyle changes and supplement intake to reduce symptoms of menopause. These treatments are an alternative for women who want to go natural and for those who have medical reasons to avoid estrogen such as history of breast cancer.
Some of the non-hormonal treatments are:
- Changing diet intake (eat foods higher in phytoestrogen such as lentils, beans and chickpeas)
- Getting regular physical activity or exercise
- Joining support groups
- Prescription medications
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Hypnotherapy
With all the different treatments out there for those undergoing menopause, do check with your medical professionals as to which one suits you the best.
Reference
1.World Health Organisation. Menopause.







