Common Questions on Prostate Cancer

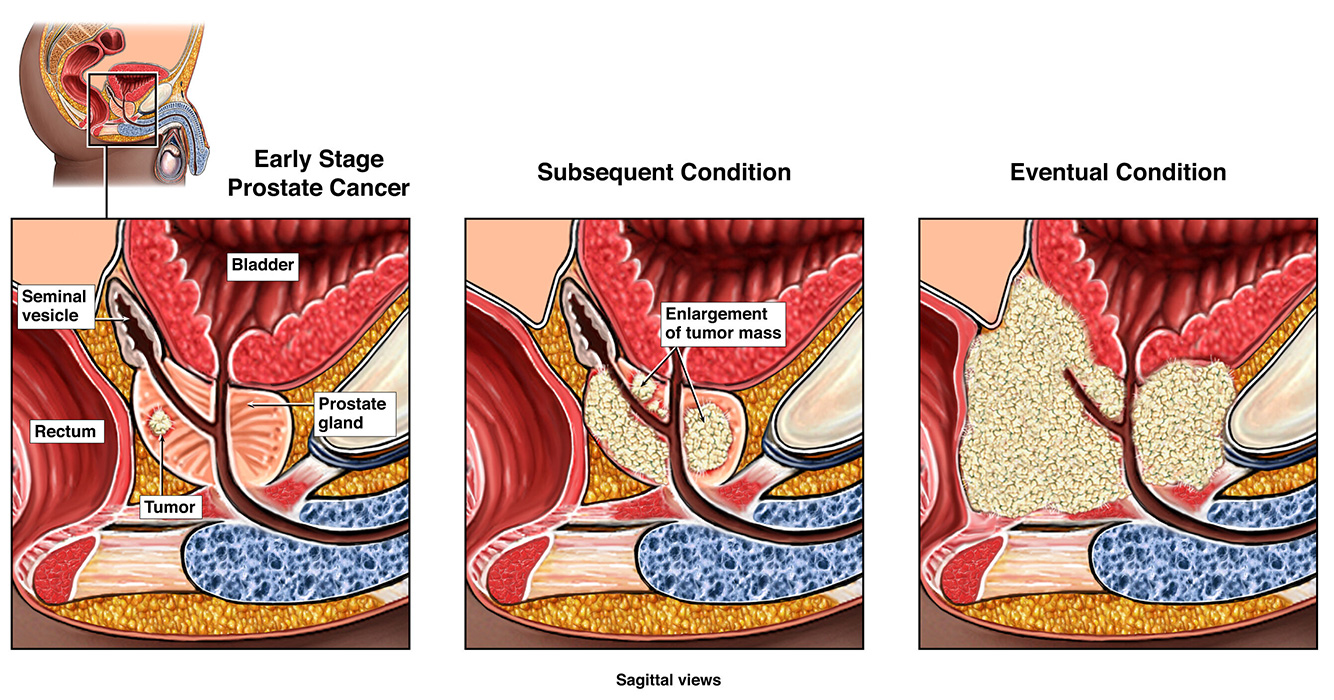
Prostate cancer begins when cells in the prostate gland start to grow out of control.
The prostate is a gland found in males only and it functions to produce and provide nourishment liquid to the sperms for energy to move across the birth canal.
If you are not aware where the prostate is, it is below the bladder (the hollow organ where urine is stored) and in front of the rectum (the last part of the intestines). The size of the prostate can change as a man ages. In younger men, it is about the size of a walnut, but it can be much larger in older men.
On this week’s posting, we share with you all about prostate cancer, it’s demographics, symptoms, treatment and detection.
1. How Common is Prostate Cancer?
 Prostate cancer is the 2nd most common cancer in men and the 4th most common cancer diagnosed worldwide.
Prostate cancer is the 2nd most common cancer in men and the 4th most common cancer diagnosed worldwide.
2. Which group of men are more likely to develop prostate cancer?
The risk factor for prostate cancer is age. The chance of being diagnosed with prostate cancer increases rapidly after age 50. About 6 in 10 of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men over the age of 65.
Prostate cancer is among the most heritable of the major human cancers; It is estimated that more than half (57%) of prostate cancer risk is due to genetic factors.

3. How treatable is prostate cancer?
More than 80% of all prostate cancers are detected when the cancer is in the prostate or the region around it, so treatment success rates are high compared to most other types of cancer in the body.
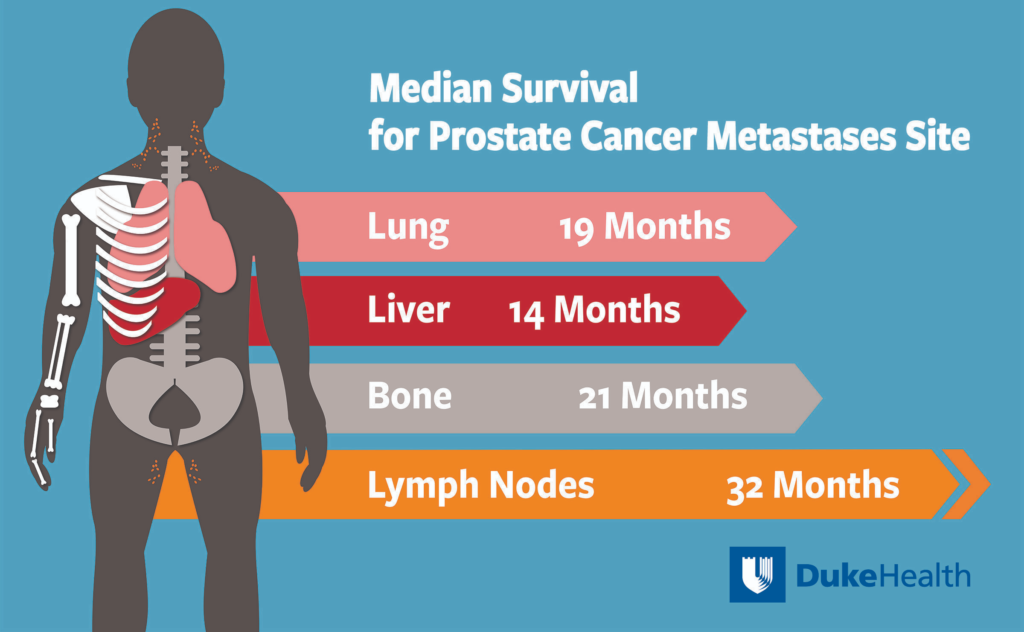
The 5-year overall survival rates for men diagnosed with local or regional prostate cancer exceed 99%. In other words, the chances of men dying from their prostate cancer is generally low. However, prostate cancer comes in many forms, and some prostate cancers can be aggressive even when they first appear to be confined to the prostate.
The survival rate of prostate cancer when it has spread to other regions of the body is 30%.
4. What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
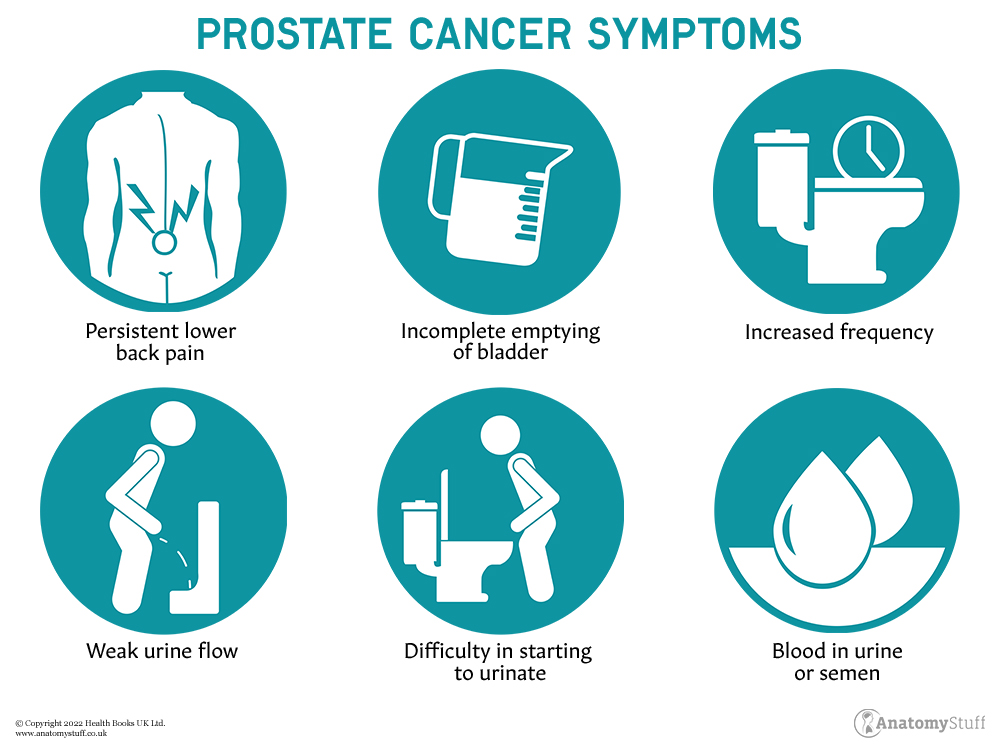
If the cancer is caught at its earliest stages, most men will not experience any symptoms. However, some men will experience symptoms such as frequent, hesitant, or burning urination, difficulty in having an erection, or pain or stiffness in the lower back, hips or upper thighs.
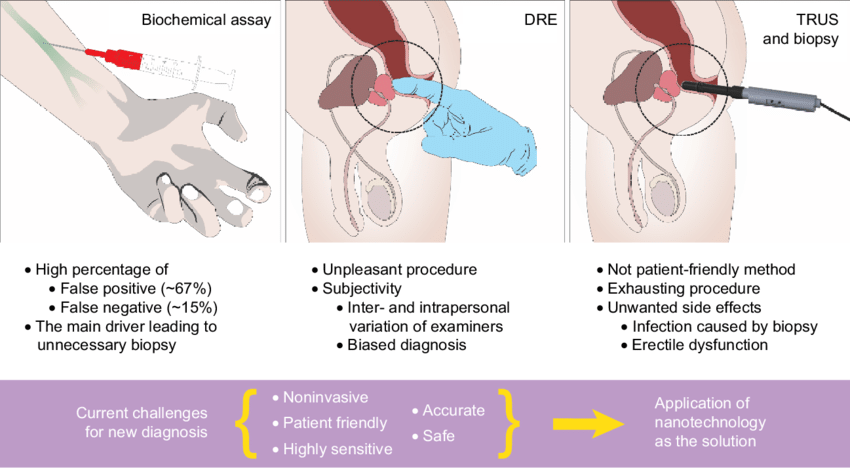
5. How is prostate cancer detected?
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) testing is the most frequent screening choice for prostate cancer. During a PSA test, a small amount of blood is drawn from the arm, and the level of PSA is measured. If prostate cancer is present, more PSA will be present in the blood.
More testing, such as digital rectal exam (DRE), imaging, and, ultimately, a biopsy, is required to confirm a diagnosis.
6. How is prostate cancer treated?
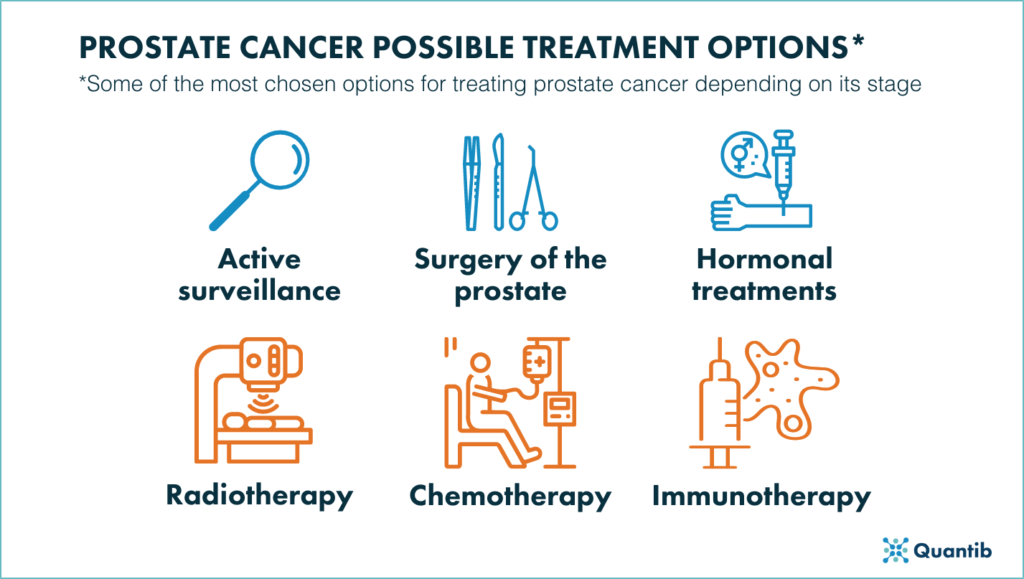
There are a wide variety of treatment options available for men with prostate cancer, including surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy and chemotherapy, any or all of which might be used at different times depending on the stage of disease and the need for treatment.
Consultation with all three types of prostate cancer specialists—a urologist, a radiation oncologist and a medical oncologist—will offer the most comprehensive assessment of the available treatments and expected outcomes.
Reference:
Prostate Cancer FAQ, Radiotherapy Clinics of Georgia







